The application process has changed dramatically throughout the years. Yet, some aspects seem eternal—like the fact that employers often start with lots of people at the top of their recruitment funnel and need to make sure they get the right people to the bottom.
But, the world is changing, and the pace of change is accelerating; candidates expect a simple, efficient recruitment process, and employers need workers who are digitally fluent and can adapt easily to change. Reskilling is also becoming even more important.
Plus, there’s also a strong focus on fairness, transparency and equality—with blind reviews of applications, diverse interview panels, and selection processes centred on the need to demonstrate competencies and alignment with the role.
Therefore, in order to adapt to today’s ever-changing landscape, it’s vital for employers to focus on a candidate’s potential to grow and adapt to future needs, as well as the skills and qualities they have today. To that end, throughout this article, we’ll share four steps for building a better assessment process—because not only is assessment the key to a more productive workforce, but it’s also essential to a workforce that’s more resilient and able to stand the test of time.
Step One: Shift from Experience to Potential
In a bid to prepare for the unknown, employers need to shift their focus away from candidates who have prior experience in a role and toward those who have potential. That’s because the employees who can demonstrate flexibility and resilience will be the ones who are best able to ride the wave of uncertainty.
Specifically, McKinsey & Company predicts that higher cognitive skills—such as creativity, critical thinking, decision-making and complex information processing—will be the most in-demand traits in the future. In fact, the need for these skills is predicted to grow by 19% in the United States and by 14% in Europe by 2030—up from already sizable demands. Furthermore, the same research also predicts the fastest rise ever in the need for advanced IT and programming skills, which could grow by as much as 90% by 2030.
As such, organisations that want to be at the forefront of innovation need to start thinking creatively about how they can tap into the vital perspectives of diverse minds. To lead a sector, outrun the competition, and truly innovate, employers need to stop looking for people who fit and start looking for people who add. Likewise, bias—conscious or unconscious—needs to be removed from the process. Besides, although they might seem like they come with a higher risk factor, people who do things very differently can create exceptional outcomes. So, instead of always asking, “Who can do the job?”, employers should be asking, “Who can take us further?”
Step Two: Reap the Rewards of Great vs. Good
Transforming candidate assessment and selection is an investment, but the business case has never been more important. Plus, many of the current processes and tools are subjective and don’t focus on differentiating between good and great hires. With this in mind, are organisations and hiring managers equipped with the tools they need to make the right decisions?
Additionally, better performance predictions will lead to better outcomes, and investing in the right tools can deliver multi-millions in cost benefits. In essence, an employer with a more agile and adaptable workforce is in a far better place to achieve competitive advantage—as well as the kind of employee satisfaction that attracts more high-achieving, agile candidates. In this way, quality hires have a substantial influence on business performance.
However, despite rigorous testing, chemistry sessions and multiple interviews, it can still be quite difficult for employers to understand whether an individual would actually be effective in a role—thereby making bad hires surprisingly common.
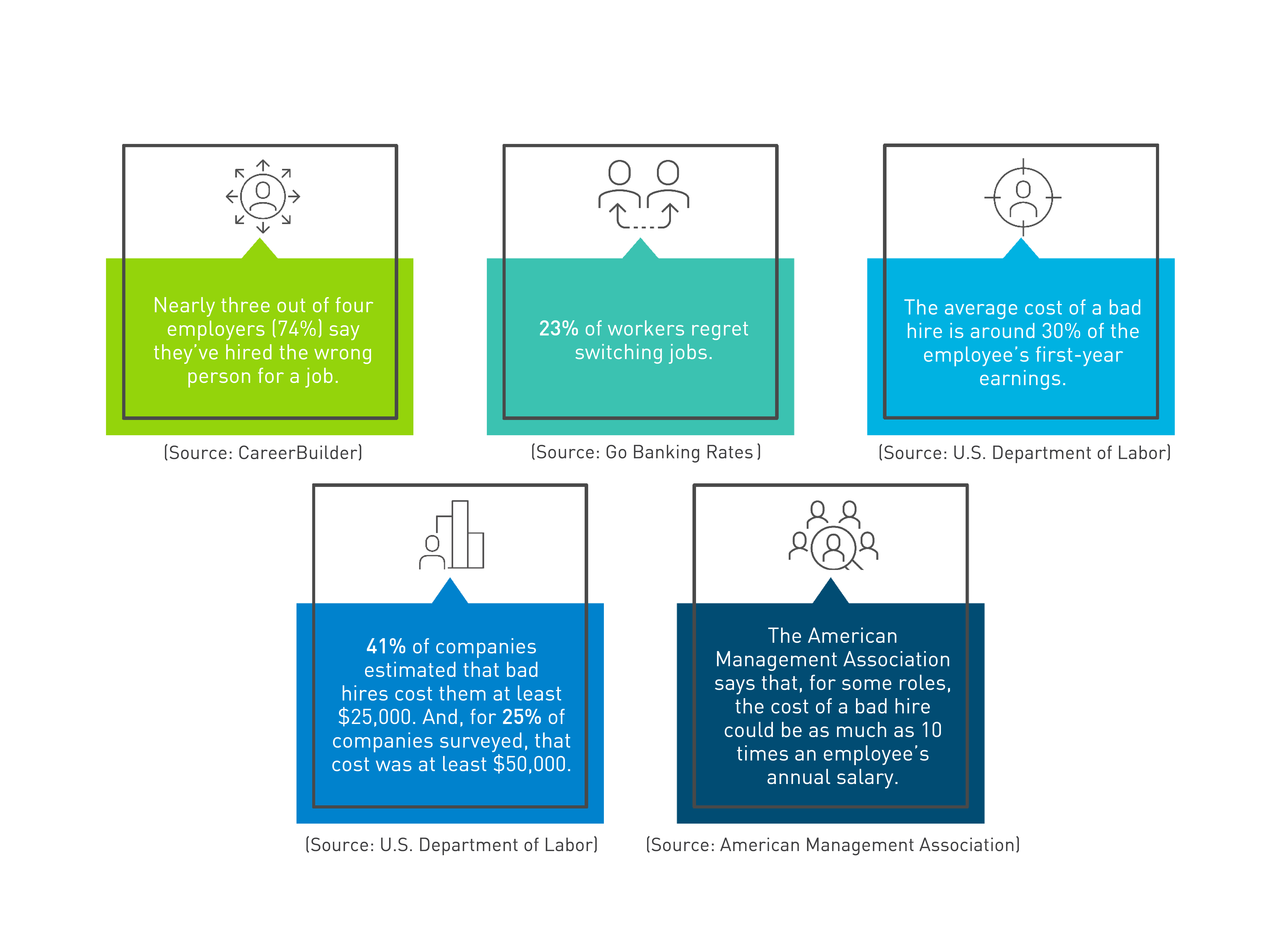
Conversely, getting great people—the people who go above and beyond the role criteria—is really good news because it has a profound effect on quality of output, which is truly beneficial to the business. What’s more, while great employees are valuable in and of themselves, they also drive wider team performance, inspire others and make it easier to recruit other great people.

Step Three: Build Better by Thinking Bigger
So, if we’re going to build a better and fairer candidate assessment process, we need to find a way to:
- Measure potential, rather than experience, because we don’t know what the future looks like.
- Identify the behaviours that are required to separate those who will actually be successful from those who present well during an interview.
- Distinguish between good candidates who meet the criteria and great candidates who will take an organisation further.
- Give candidates a clear and authentic picture of the organisation and the role so that they can self-select out of the process if the opportunity isn’t right for them.
- Include candidates who might have non-traditional experiences or career paths and assess them equally.
- Assess candidates fairly and without subjectivity or bias.
Finally, employers need to be able to identify and select candidates who are motivated and energised to be productive at work. And, the way that we do all of these things is by assessing for passion, purpose and mindset.
Assessing Passion, Purpose & Mindset
Traditional assessment processes assess for capability, behaviour and results. These terms are defined as:

Then, when these aspects are combined with new measurements that focus on purpose, passion and mindset, we can better predict the success of candidates and determine the candidates who are more engaged and likely to be a better hire for employers.
Let’s dig into those new descriptors and what they mean.
Purpose
Purpose is a candidate’s alignment with and willingness to contribute to the vision and values of an organisation. For example, one study reported by McKinsey found that, out of 100 variables, employees reported that seeing purpose and value in their work was their most motivating factor—even more so than compensation. Notably, this is especially important for younger workers.
Clearly, ensuring that applicants understand the organisation’s purpose and consider how aligned they are with that throughout the assessment process engenders a sense of belonging and partnership that underlies both great performance and job satisfaction.
In this way, assessment tools can be built around the organisation’s vision and values so applicants have a chance to form an appreciation of them from their earliest contact with the organisation. Then, if they don’t share the same values, they can choose another path. However, applicants who see an affinity with their own values will begin to feel the engagement and inspiration that will drive job success and satisfaction—even before they’re hired.
Passion
Passion is a candidate’s enthusiasm, enjoyment and commitment to mastering the requirements of a role. When an employee is passionate about a role, they’re engaged. Even so, most employers don’t have a method to effectively understand what a candidate is passionate about.
For this reason, during the assessment stage, employers need to find ways to reveal an applicant’s natural passions—which are often in the form of strengths—and find out if these are aligned with the role requirements. Then, they’ll be able to determine whether the candidate is likely to be a high performer who will want to commit the effort needed to succeed in all aspects of the job. Interviews, assessment centre exercises, and immersive online assessments are excellent vehicles for exploring and observing applicants’ innate strengths in relation to the role. Similarly, self-evaluation tools can also be used to help applicants consider their own strengths and whether the role will offer sufficient opportunity to use and demonstrate them.
Mindset
Mindset is a candidate’s belief about themselves and their basic qualities, although these beliefs are rarely measured by employers. The two types are defined as:
Fixed mindset: The belief that one’s talents are innate gifts and not malleable.
Growth mindset: The belief that one’s talents can be developed through education and effort.
It’s thought that people with a growth mindset achieve greater success because they’re focused on learning and believe that they can get better and develop new skills. It’s worth noting here that organisations can have a growth mindset, too. For instance, organisations with a growth mindset are more likely to fill vacancies internally, whereas organisations with a fixed mindset automatically advertise in the external market.
When assessing mindset, we’re looking to understand a candidate’s strengths and attitudes in relation to learning, feedback, resilience and adaptability. Of course, there are many ways to do that; just keep in mind that it’s less about what candidates may have done in the past and more about how they approach their work and develop and broaden their competence.
Step Four: Think Outside the Checkbox
By focusing purely on the capability, behaviour and results of candidates as they’re presented in front of the recruitment team, today’s more traditional interview and assessment process can be challenging for both candidates and employers. That’s because, while these measures can predict the future success of certain candidates in specific roles, change is now constant—which means that better, more well-rounded assessments are a must.
For instance, a more blended assessment during the pre-screening allows employers to shortlist candidates based on several different attributes at the same time. The candidate can then forego multiple stages by demonstrating different attributes at the same time. This way, employers can get a clear picture of the different strengths and weaknesses of the entire group of candidates in order to make informed decisions about which candidates are best to bring forward to the interview stage.
The talent landscape and the world around us renders current assessment processes ineffective. As such, employers need to embrace a new approach that both ensures that candidates are assessed appropriately and also empowers them to make good decisions.
To that end, passion, purpose, and mindset can have as much influence on performance as a candidate’s core intellect, achievements and behaviours. And, by building these factors into the assessment of a potential employee, employers can select from a diverse pool of candidates based on each individual’s potential, as well as their current performance.
Unfortunately, most employers aren’t assessing for all of these factors, so they’re missing out on a comprehensive look at candidates. In the end, the question your organisation needs to consider is this: In a rapidly changing world, what is the cost of maintaining the status quo?
To learn more about how to build the specific assessments to fit your needs, download our ebook.



